How to ensure welding quality when using Socket Fusion Welding Machine?
Equipment Preparation
Before using a Socket Fusion Welding Machine for pipe welding, equipment preparation is the primary step to ensure welding quality. The condition of the equipment directly affects the stability of the weld and joint strength, so a thorough inspection and adjustment must be performed before each operation.
Cleaning the Heating Plate and Tools
If the heating plate has dust, welding residue, oil, or scratches, it can cause uneven pipe melting, leading to voids or weak welds. Before operation, wipe the heating plate with a clean lint-free cloth or a dedicated cleaning agent, ensuring the surface is smooth and undamaged.
Selecting the Correct Socket and Dies
Socket fusion machines are equipped with dies of various sizes, each corresponding to a specific pipe diameter. Using the wrong size may prevent proper pipe insertion or sufficient weld depth, affecting the joint strength. Therefore, select the corresponding socket dies and accessories based on the pipe specifications and wall thickness.
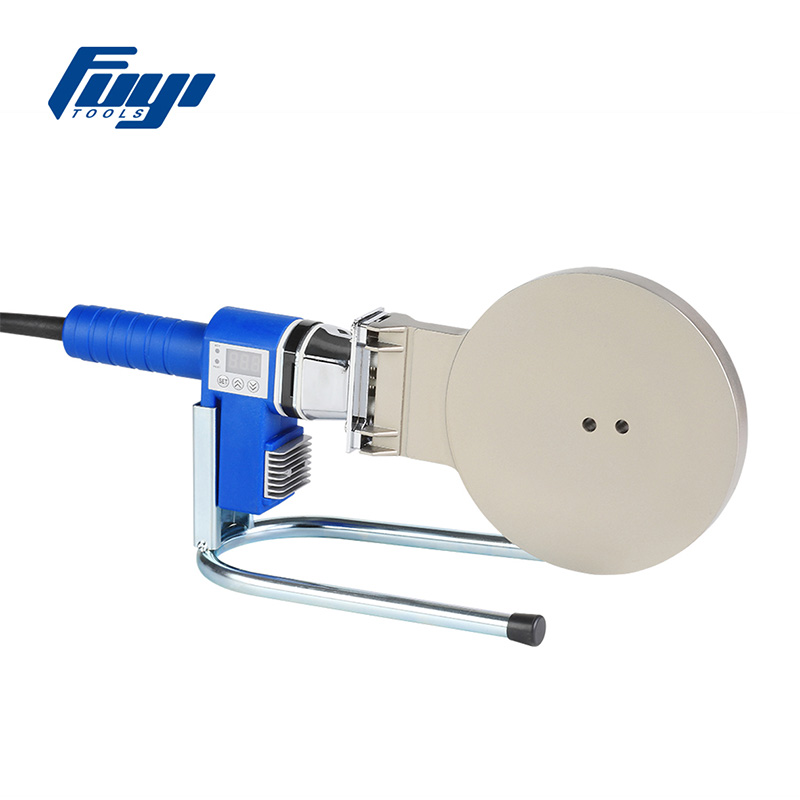

Machine Calibration
Different pipe materials and wall thicknesses require different welding temperatures and heating times. Before operation, verify that the machine temperature settings are correct. For example:
- PP-R pipes: approximately 260 °C
- PE pipes: approximately 220 °C
Incorrect temperatures can cause pipe deformation or insufficient fusion. Regularly check the temperature control and timing devices to ensure stable machine operation.
Check for Wear and Tear
Long-term use may cause wear on the machine, such as worn heating plates or loose handles, affecting welding quality. Inspect the equipment carefully before use and replace or maintain any worn parts.
Material Preparation
Proper preparation of the pipe and fittings before welding is equally critical. Even with a well-maintained machine, dirty surfaces or inaccurate cuts can compromise weld quality.
Cutting Pipe Ends
Pipe ends must be cut using a proper pipe cutter to ensure a square and smooth cut. Angled or serrated cuts can prevent the pipe from fully inserting into the socket, leading to leaks or stress points.
Removing Burrs and Debris
After cutting, burrs or plastic shavings may remain on the pipe. Welding without removing them can create weak points. Use a deburring tool to smooth the pipe ends.
Cleaning the Surfaces
Pipe surfaces must be clean, free of dust, oil, or moisture. Contaminants can interfere with melting, creating voids or weak welds. Wipe the pipe ends with a dry cloth or lint-free paper, and use alcohol if necessary.
Temperature Control
Temperature is a core factor in socket fusion welding, and improper control is a common cause of weld failure.
Preheating the Machine
Ensure the machine reaches the target temperature before welding. Insufficient temperature results in incomplete melting, while excessive temperature can over-melt the pipe surface, causing deformation or shrinkage.
Avoid Overheating
Different pipe materials have different heat sensitivities. Strictly follow the manufacturer’s recommended temperature ranges. Reference temperatures for common pipe materials are shown below:
| Pipe Material | Recommended Temperature | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| PP-R | 260 °C | High temperature, short welding time, prevent oxidation |
| PE | 220 °C | Low temperature, slow welding, prevent deformation |
| PVDF | 270 °C | Chemically resistant, precise temperature control required |
Temperature Monitoring
It is recommended to continuously monitor the machine temperature during welding to prevent large fluctuations. For long-duration work, an independent thermometer or thermocouple can measure the actual heating plate temperature to ensure process stability.
Welding Procedure
A standardized welding procedure is crucial to ensure weld quality. Each step must be executed precisely to avoid human error.
Align the Pipe and Fitting
The pipe and fitting must be aligned along the axis. Even slight tilting or misalignment can lead to uneven welds and stress concentration, reducing strength.
Insert the Pipe
Insert the pipe evenly into the socket without excessive force or tilting. Ensure the pipe reaches the specified depth to achieve proper fusion.
Control Welding Time
Welding time includes both heating time and cooling time:
- Heating time: Usually calculated per millimeter of pipe wall thickness. Too short means insufficient melting; too long can deform the pipe.
- Cooling time: Allow the pipe to sit undisturbed until fully cooled. Moving or rotating the pipe can cause cracks in the weld.
Prevent Movement
Do not rotate or shake the pipe during welding, as this can create gaps in the weld and weaken it.
Post-Weld Inspection
After welding, inspection and verification are essential to ensure quality.
Visual Inspection
Check the weld appearance for uniformity, completeness of the weld bead, and absence of depressions, cracks, or residual debris.
Mechanical Strength Testing
For critical pipelines, conduct pressure tests or peel tests to ensure the joint strength meets design requirements.
Record Keeping
Document the welding temperature, time, pipe model, and operator for quality tracking and management purposes.
Operator Training
Operator skill directly affects weld quality and requires professional training.
Familiarity with Procedures
Operators should understand the machine operation, welding parameters for different pipe materials, and proper heating, insertion, and cooling procedures.
Strictly Follow Standards
Adhere to construction standards and manufacturer-recommended procedures. Avoid altering temperature, time, or steps arbitrarily.
Experience Accumulation
Through practice, operators can identify abnormal phenomena during welding and take timely measures to prevent defective joints.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Related Products
 +86-158 6813 9123
+86-158 6813 9123 +86-571- 82432777
+86-571- 82432777 [email protected]
[email protected] No.7 Yangguang Road, Linpu Industrial Area, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
No.7 Yangguang Road, Linpu Industrial Area, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
Copyright © 2024 Hangzhou Fuyi Tools Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
|
 Eng
Eng  русский
русский Español
Español












